Reflection Of Sound
Reflection of Sound and Its Application
Sound: Definition
Sound is defined as oscillations or auditory sensations evoked by oscillations in particle displacement or velocity, propagated in a medium with internal force. Sound propagates as a mechanical wave, through a medium such as air or water.
Reflection of Sound
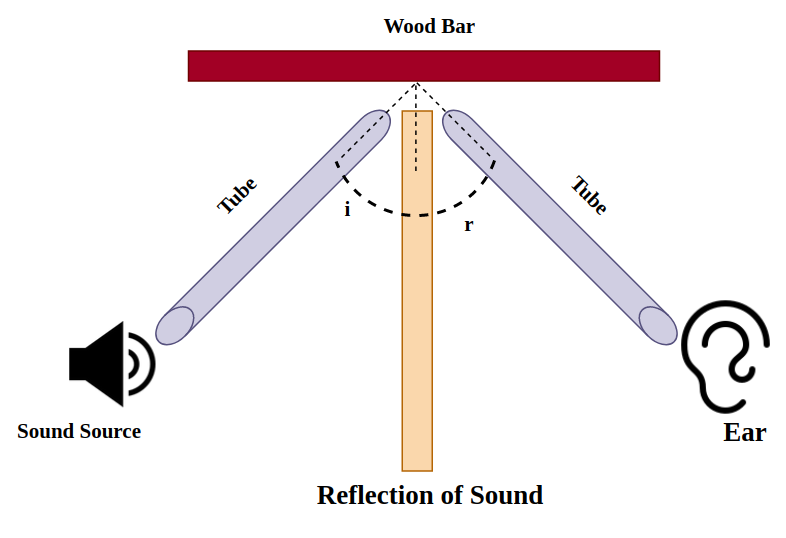
Just like the reflection of light, the reflection of sound is similar as it follows the laws of reflections, where the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence and the reflected sound, the incident sound, and the normal sound belong in the same plane. Sound bounces off the surface of the medium which can be a solid or a liquid. In order to make the reflection of sound to occur, the surface can be of large size and can be either rough or polished.
Laws of Reflection of Sound
The angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence . The reflected sound, the incident sound, and the normal sound belong in the same plane. Read More: Angle of Incidence
Applications of Reflection of Sound
Echo:
The sound heard after reflections from a rigid surface such as a cliff or a wall is called an echo creating a persistence of sound even after the source of sound has stopped vibrating. The echo is used by bats and dolphins to detect obstacles or to navigate. The same principle is used in SONAR (Sound Navigation And Ranging technique), used in oceanographic studies. SONAR is used for the detection and location of unseen underwater objects, such as submerged submarines, sunken ships, and icebergs. In SONAR, ultrasonic waves are sent in all directions from the ship and the received signal is analysed.
Hearing Aid:
A hearing aid is a device used by people with difficulty in hearing. Here, the sound waves are received by the hearing aid and are reflected in a narrower area leading to the ear.
Megaphone:
Megaphones are horn-shaped tubes that prevent the spreading out of sound waves by successive reflections, thus confining them to the air in the tube.
Sound Board:
Sound boards are curved surfaces that are placed in such a way that the sound source is at the focus. The sound waves are made to reflect equally throughout the hall or an auditorium thus enhancing their quality.