Rate of Change of Velocity
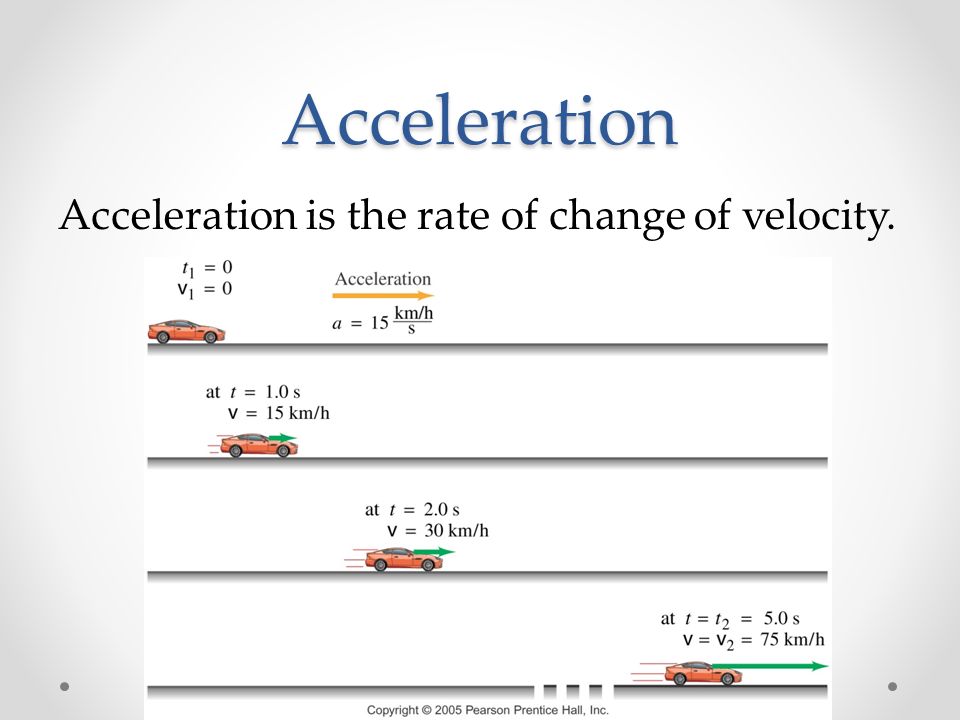
Acceleration An object is said to be accelerated if there is a change in its velocity. The change in the velocity of an object could be an increase or decrease in speed or a change in the direction of motion. A few examples of acceleration are the falling of an apple, the moon orbiting around the earth, or when a car is stopped at the traffic lights. Through these examples, we can understand that when there is a change in the direction of a moving object or an increase or decrease in speed, acceleration occurs.
What Is Acceleration?
Acceleration is defined as The rate of change of velocity with respect to time. Acceleration is a vector quantity as it has both magnitude and direction. It is also the second derivative of position with respect to time or it is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time.
What Is the Unit of Acceleration?
The SI unit of acceleration is given as:
SI unit - m/s2
Types of Acceleration
Uniform and Non-uniform Acceleration
So can we have a situation when speed remains constant but the body is accelerated? Actually, it is possible in a circle where speed remains constant but since the direction is changing hence the velocity changes, and the body is said to be accelerated.
Average Acceleration The average acceleration over a period of time is defined as the total change in velocity in the given interval divided by the total time taken for the change. For a given interval of time, it is denoted as ā.
What Is Instantaneous Acceleration?
Instantaneous acceleration is defined as The ratio of change in velocity during a given time interval such that the time interval goes to zero.
Related Articles:
Angular Acceleration
What is Velocity?
Velocity-Time Graph
accelerationAverage acceleration: In the velocity-time graph shown above, the slope of the line between the time interval t1 and t2 gives the average value for the rate of change of velocity for the object during the time t1 and t2.
Instantaneous acceleration: In a velocity-time curve, the instantaneous acceleration is given by the slope of the tangent on the v-t curve at any instant.
Positive, Negative and Zero Acceleration
Consider the velocity-time graph shown above. Here, between the time intervals of 0-2 seconds, the velocity of the particle is increasing with respect to time; hence the body is experiencing a positive acceleration as the slope of the v-t curve in this time interval is positive. Between the time intervals of 2-3 seconds, the velocity of the object is constant with respect to time; hence the body is experiencing zero acceleration as the slope of the v-t curve in this time interval is 0.
Now, between the time intervals of 3-5 seconds, the velocity of the body is decreasing with respect to time; hence the body experiences a negative value of the rate of change of velocity as the slope of the v-t curve in this time interval is negative.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q1 What is centripetal acceleration?
When an object is moving in a circle and its acceleration vector is pointed towards the centre of that circle, it is known as centripetal acceleration. The unit of centripetal acceleration is m/s2.
Q2 What is gravitational acceleration?
Gravitational acceleration is used for indicating the intensity of the gravitational field. It is expressed as m/s2 and its value on the surface of the earth is 9.8 m/s2.
Q3 What is tangential acceleration?
Tangential acceleration is defined as the rate of change of the tangential velocity of a particle in a circular orbit. There are 3 possible values for tangential acceleration. First, when the magnitude of the velocity vector increases with time, tangential acceleration is greater than zero. Second, when the magnitude of the velocity vector decreases with time, tangential acceleration is less than zero. The third possibility is when the magnitude of the velocity vector remains constant, the tangential acceleration is equal to zero.
Q4 What is radial acceleration?
When there is an acceleration of an object along the radius directed towards the centre, it is known as radial acceleration. It is expressed as radian/sec2.
Q5 What is Coriolis acceleration?
The acceleration due to the rotation of the earth is known as the Coriolis acceleration. This acceleration is experienced by the particles that move along the surface of the earth.