Oxidation and reduction
Oxidation and Reduction Reaction
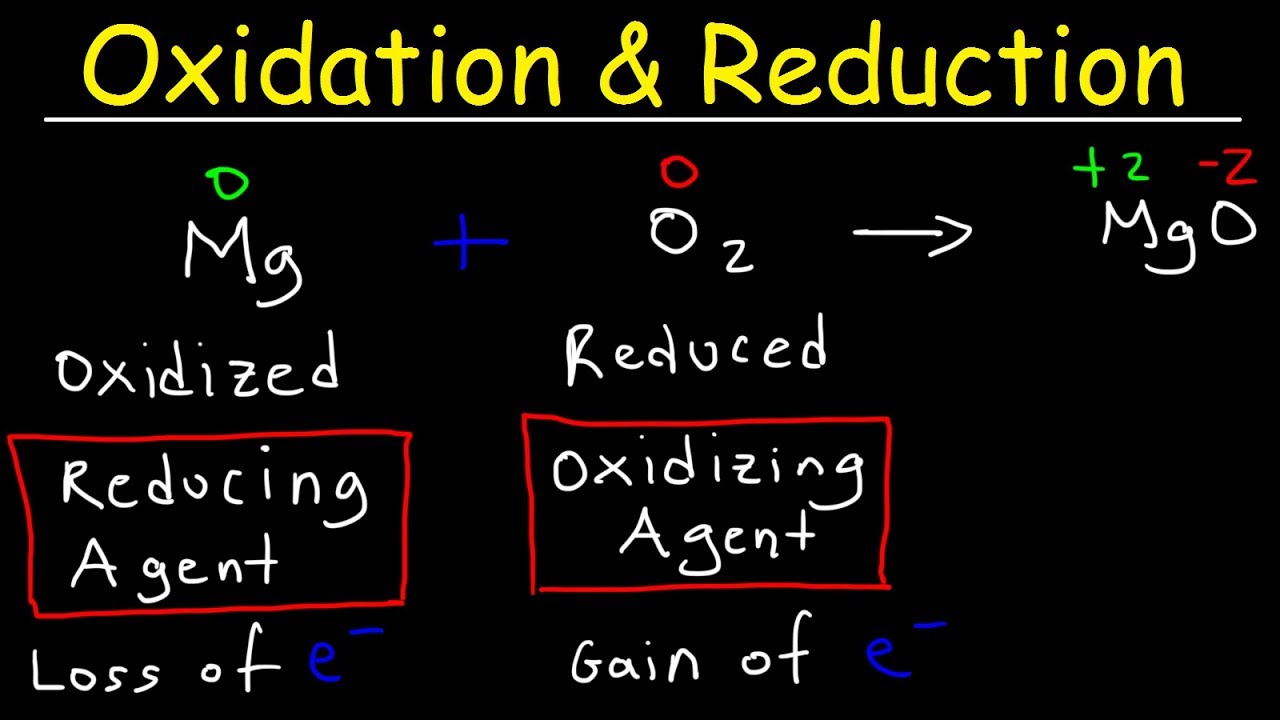
We get to hear the terms like oxidation and reduction a lot in CBSE class 12th Chemistry and to be precise, oxidation means gaining oxygen in a chemical reaction We will be looking at oxidation and reduction from two different points of view. The chemical reactions which involve the transfer of electrons from one chemical substance to another. These electron-transfer reactions are termed as oxidation-reduction reactions or redox reactions. These reactions are accompanied by energy changes in the form of heat, light, and electricity etc. The oxidation and reduction reaction also involve the addition of oxygen or hydrogen to different substances.
According to Classical or earlier concept oxidation is a process which involves the addition of oxygen or any electronegative element or the removal of hydrogen or any electropositive element. According to electronic concept oxidation is defined as the process in which an atom or ion loses one or more electrons.
What is Reduction?
According to Classical or earlier concept reduction is a process which involves the addition of hydrogen or any electropositive element or the removal of oxygen or any electronegative element. According to electronic concept reduction is defined as the process in which an atom or ion gains one or more electrons.
Classical Idea of Oxidation and Reduction reactions:
Oxidation reactions involve:
1. Addition of oxygen:
C + O2 → CO2 (oxidation of carbon)
2. Addition of electronegative element
Fe + S → FeS (oxidation of Iron)
3. Removal of hydrogen
H2S + Br2 → 2 HBr + S (oxidation of sulphide)
4. Removal of electropositive elements
2 KI + H2O2 → I2 + 2 KOH (oxidation of iodide)
Oxidising agent is a substance which brings about oxidation. In the above examples O2, S, Cl2, Br2, and H2O2 are oxidising agents.
Reduction reactions involve
1. Addition of hydrogen
N2 + 3 H2 → 2NH3 ( reduction of nitrogen) 2. Addition of electropositive element
SnCl2 + 2HgCl2 → SnCl4 + Hg2Cl2 ( reduction of mercuric chloride)
3. Removal of oxygen
ZnO + C → Zn + CO (reduction of zinc oxide)
4. Removal of electronegative element
2FeCl3 + H2 → 2FeCl2 + 2HCl (reduction of ferric chloride)
Reducing agent is a substance which brings about reduction. In the above examples H2, HgCl2 and C are Reducing agents.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q1 What is the difference between oxidation and reduction?
It loses electrons in a reaction in chemistry if a substance is oxidized. It gains electrons in a reaction if a substance is reduced. A reaction within which there is both oxidation and reduction is called a REDOX reaction.
Q2 Why are oxidation and reduction Important?
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions are significant because they are the main natural or biological and artificial energy sources on this planet. Oxidation of molecules usually releases large amounts of energy by removing hydrogen and replacing it with oxygen.
Q3 What is the oxidation-reduction process?
It oxidizes the material that gives electrons. It forms a chemical called rust when iron reacts with oxygen because it has been oxidized (the iron has lost some electrons) and the oxygen has been reduced (the oxygen has gained some electrons). The cause of reduction is oxidation.
Q4 What is called the oxidation state?
The oxidation state, also referred to as the amount of oxidation, defines a chemical compound’s degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom. Antoine Lavoisier first used the term oxidation to describe a substance’s reaction with oxygen.
Q5 What is an example of slow oxidation?
Iron rusting and wood-rotting are good examples of gradual oxidation.
Q6 What is meant by the oxidation-reduction reaction?
A chemical reaction where the oxidation number of an atom, ion, or molecule changes by losing or gaining an electron is called an oxidation-reduction reaction.
Q7 What is the major difference between oxidation and reduction?
Reduction is the gain of electrons whereas oxidation is the loss of electrons.