Metals and nonmetals
What are Metals?
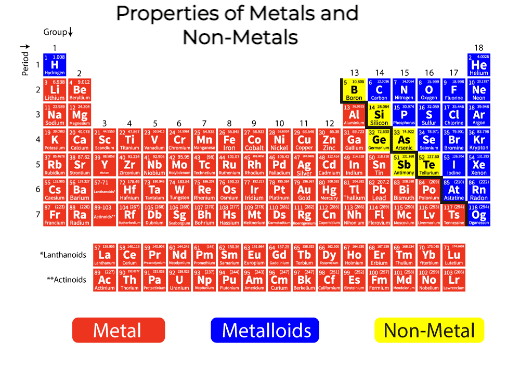
The Majority elements in the periodic table are metals. This includes alkali metals, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides and alkaline earth metals. Metals are separated by nonmetals on a periodic table through a zigzag line starting from carbon, till radon. The elements between the two are phosphorus, selenium and iodine. These elements and elements right to them in the periodic table are nonmetals. Elements present just to the left of the line are termed as semimetals or metalloids. These will have the combined properties of both metals and nonmetals.
Metals and Non-metals One-Shot
Non-metals occupy the upper right-hand portion of the periodic table. Considering the properties of non-metals it is not shiny, malleable or ductile nor are they good conductors of electricity. These properties of non-metals provide one means by which we can distinguish metals from non-metals. Properties of Non-metals have less in common with each other than metals. Their physical and chemical properties vary widely. Some non-metals are solids and some are gases at room temperature.
What are Non metals?
Very few elements in the periodic table are non-metals. These are present on the right-hand side in the periodic table. Elements that come under non-metals are sulphur, carbon, all halogens, phosphorus, hydrogen, oxygen, selenium, nitrogen and noble gases. In the periodic table, non-metals are located left of the halogens and to the right of the metalloids. Since noble gases and halogens are also non-metals, these elements are often referred to as non-metals.
Properties of Metals
Physical Properties of Metals Some physical properties of metals are listed below. Shiny (lustrous) in nature Metal is a good conductor of electricity and heat Density and melting point is high Mouldable (Malleable) Ductile At room temperature, it is in solid form except for mercury Opaque
Chemical Properties of Metals Some chemical properties of metals are listed below. Easily corrodible Can lose electrons Form basic oxides Have low electronegativities Good reducing agents
Properties of Non-Metals
Physical Properties of Non-metals
Some physical properties of non-metals are listed below. Poor conductors of electricity and heat Non-Ductile metals Brittle solids Maybe solids, liquids or gases at room temperature These are not sonorous Transparent
Chemical Properties of Non-metals
Some chemical properties of non-metals are listed below. The number of electrons in the outer shell is generally 4-8 Easily gain or lose valence electrons Form acidic oxides whenever they come in contact with oxygen High electronegative elements Great oxidizing agents
Properties Of Metals And Non-Metals
Physical Properties of Metals and Non-metals
The metals have a lustrous surface; they can also be polished for obtaining a highly reflective surface. Metals are hard and strong in nature. Sodium and potassium are exceptions in this case as they can be cut by a knife. Metallic elements possess high melting and boiling points. They can vaporize too at high temperatures. Their density is also high. The metals are malleable and ductile that is they can be beaten into sheets or drawn into wires. They are excellent conductors of heat and electricity. On the other hand, non-metallic elements are bad conductors of heat and electricity, except graphite (an isotope of carbon). They are neither malleable nor ductile. Non-metals possess low density and have low melting and boiling points. They are soft solids, except diamond which is the hardest substance known.
Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-metals
Metallic elements generally have 1, 2 or 3 electrons in the outermost shell. Lesser the number of valence electrons more is the activity of the metal. They form cations by losing electrons. The molecule of metals in the vapour state is generally mono atomic. They generally form basic oxides. They ionize by losing electrons hence, they are known as reducing agents. Non-metallic elements generally have 5, 6 or 7 electrons in their outermost shell. They form anions (negative ions) by gaining electrons to complete their octet. Their molecules are usually polyatomic in the gaseous state. They generally form acidic oxides. Non-metals ionize by the gain of electrons hence, they are known as oxidizing agents.