Dispersion Of White Light By a Glass Prism and Scattering of Light
Dispersion Of White Light By a Glass Prism
What is Prism?
In optics, a prism is defined as a transparent solid body that has three rectangular lateral surfaces and two triangular faces that are inclined at an angle. The angle at which the surfaces are inclined is known as the angle of the prism. It is also known as refracting angle. The other important term in the prism is the angle of deviation of a prism. It is defined as the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray. Following is the formula used for calculating the angle of deviation:
i1 + i2 = A + δ
Learn how to trace the path of the rays using a glass prism here.
What is Dispersion?
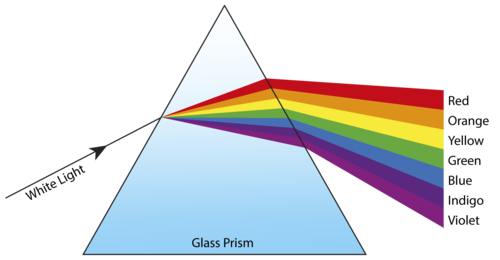
Dispersion is defined as the separation of white light into different colours when the light is passed through the prism. The scattering of light depends on the wavelength of the light. Therefore, it can be said that the degrees of deviation is dependent on the wavelengths. The deviation in the path of the light is inversely proportional to the wavelength. White light is primarily composed of light of different wavelengths (colours) viz. violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, and red with red having the highest wavelength while violet having the lowest wavelength. Red light suffers the least amount of deviation and violet the most. Since all the wavelengths suffer different angles of deviation, when white light passes from one optical medium to another, different colours of the light split, and this phenomenon of splitting of light into its components as result refraction is called dispersion.
Dispersion of White Light by a Glass Prism
When white light is made to pass through a prism, a spectrum of seven colours is formed which shows that white light is a mixture of seven different colours. Prism only acts as a medium for the separation of the seven colours. When light falls on the glass prism, refraction takes place. Since the wavelength of different components of light is different and the frequency is constant, each component gets deviated by a different angle due to the difference in velocity in the glass medium. The red colour having the maximum wavelength deviates the least and forms the upper part of the spectrum whereas violet having the least wavelength deviates the most.
Advanced Sunrise and Delayed Sunset
Did you know that we actually see the sunrise about 2 minutes earlier than the actual sunrise? Also, the sunset that we witness is of the sun that has already set? It is fascinating to learn that the position of the sun varies so much from its actual position. This is because of the phenomenon known as atmospheric refraction.
What Is Refraction?
Read More: Refraction of Light
What is Atmospheric Refraction?
Atmospheric refraction is defined as the refraction of light by the earth’s atmosphere. The earth’s atmosphere has different layers with different optical densities. When an object transmits light rays in the atmosphere, the light travels through these different layers and gets refracted.
Advanced Sunrise Explanation During sunrise, the sun is rising above the horizon. The rays from the sun get refracted as they travel from more dense air to less dense air. Also, the human eye sees the sun rays as a straight line, which appears as the sun has risen. But it has actually not yet risen.