Carbon compounds And Difference between saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons
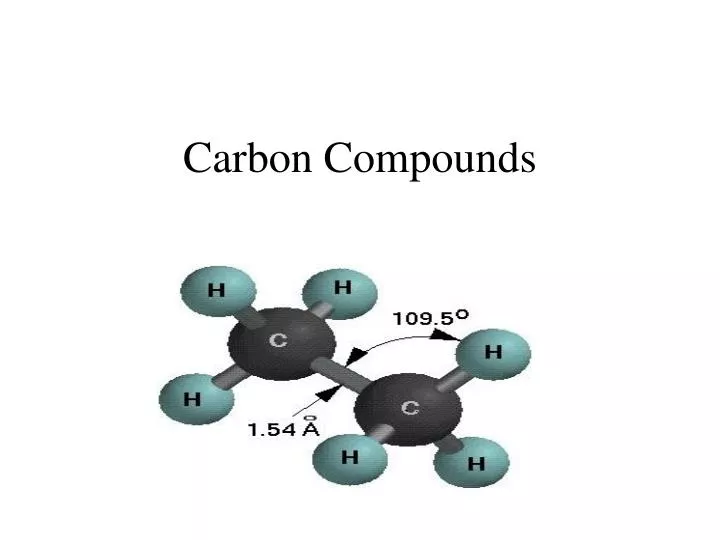
Carbon compounds
Carbon is very reactive. It forms a huge number of compounds with many other elements. Compounds containing carbon outnumber the compounds of all the other elements. Carbon is known to form a number of compounds due to the salient properties it carries with itself. The most general or the basic compound formed by carbon is methane (CH4). Such types of compounds formed by the combination of hydrogen and carbon are known as hydrocarbons. You can easily guess the molecular formula of such type of compounds by just adding hydrogen to satisfy the valency of carbon atoms.
Ethane which has two carbon atoms will need 6 hydrogen atoms to satisfy the valency of each carbon atom (keeping in mind the single bond existing between both the carbon atoms). Hence, the molecular formula for ethane is C2H6. Now, the bond between two or more carbon atoms involved in the formation of a compound can be single, double or even a triple bond. Thus, on the basis of the number of bonds existing between the C-atoms involved in the formation of a compound we classify carbon compounds into two major categories: saturated and unsaturated carbon compounds.
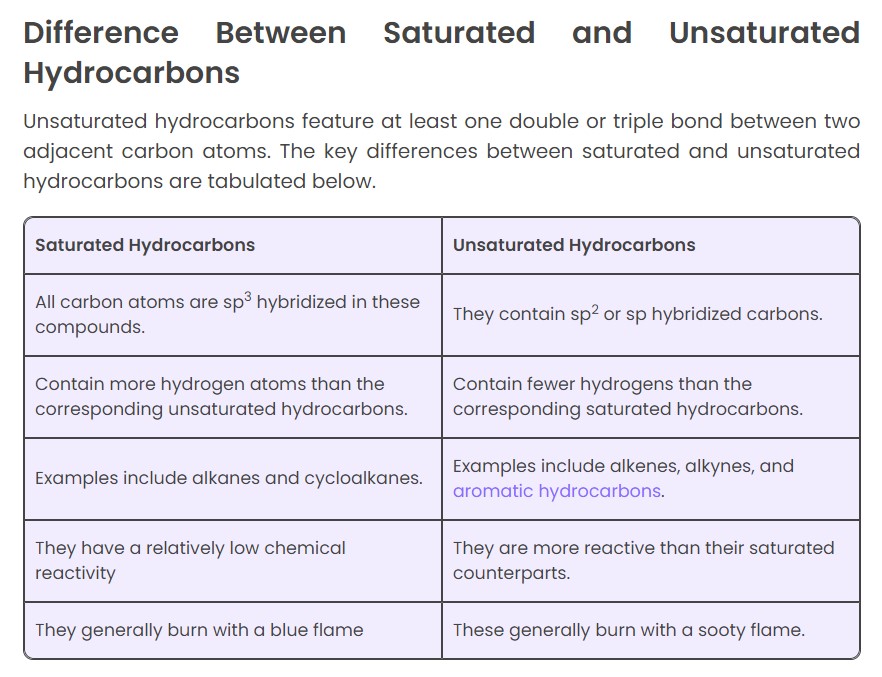
Types of Carbon Compounds
1. Saturated Carbon Compounds
2. Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
Catenation Property of Carbon
One of the most amazing properties of carbon is its ability to make long carbon chains and rings. This property of carbon is known as catenation. Carbon has many special abilities out of all one unique ability is that carbon forms pπ-pπ bonds which are nothing but double or triple bonds with itself and with other electronegative atoms like oxygen and nitrogen. Just because of these two properties of carbon i.e catenation and multiple bond formation, it has the number of allotropic forms. The Existence of Carbon Compounds Carbon is one of the more widespread heavy elements – it may make up almost 0.5 percent of the universe mass. The solar system formed from a material that was quite rich in carbon. Even then the element only makes up 0.025 percent of Earth’s crust and most of this carbon bound up in rocks and minerals such as limestone and chalk. But carbon is highly concentrated in living creatures and accounts for nearly one-quarter of atoms in our tissues.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q1 Which is an ionic compound?
Ionic compounds are ion compounds. These ions are atoms that gain or lose electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Metals tend to lose electrons, so they have a net positive charge and become cations. Non-metals tend to gain electrons, creating a net negative charge of anions.
Q2 What are the common ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds have high points of melting and boiling and appear to be strong and brittle. Ions may be single atoms, such as sodium and chlorine in common table salt (sodium chloride) or more complex groups such as calcium carbonate.
Q3 What is the ionic bond example?
The ionic bond concept is when a positively charged ion forms a bond with a negatively charged ion and one atom passes electrons to another. An example of an ionic bond is Sodium Chloride, a chemical compound.
Q4 Is MgO an ionic compound?
To have an octet, Mg loses two electrons. To have an octet, oxygen gains two electrons. The ionic bond between ions is the result of opposite charges being applied electrostatically. The final magnesium oxide formula is MgO.
Q5 What are the 2 parts of an ionic compound?
Ionic compounds are compounds made up of ions that form charged particles when an atom (or group of atoms) gains or loses electrons. A cation is an ion charged positively; an anion is an ion charged negatively.