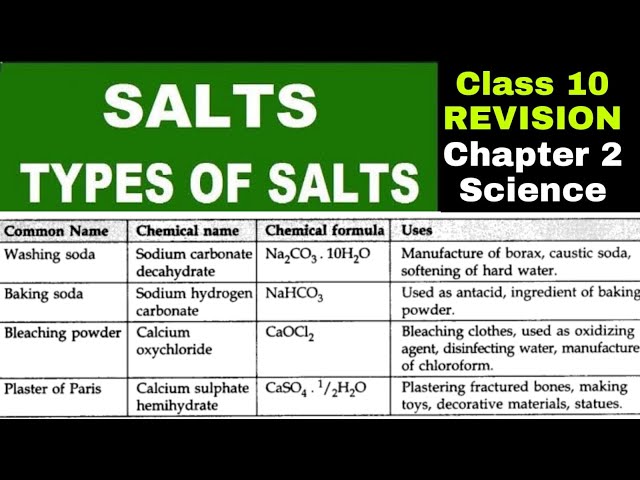
Bleaching powder, Baking soda and Washing soda
What is the Chemical Name of Bleaching Powder?
The chemical name of bleaching powder is calcium hypochlorite
Common Salt (Sodium Chloride)
Common salt is formed by the reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide. Its chemical name is sodium chloride (NaCl).
Bleaching Powder
Bleaching powder is a pale yellowish powder existing with a strong smell of chlorine. It is soluble in water but due to the presence of impurities, we never observe a clear solution. Its chemical formula is Ca(OCl2) with its chemical name Calcium hypochlorite. Calcium hypochlorite Calcium hypochlorite
1. Preparation of Bleaching Powder
Bleaching powder is synthesized by the action of chlorine gas (produced from the chlor-alkali process) on dry slaked lime (Ca(OCl2)).
2. Uses of Bleaching Powder It is used for bleaching dirty clothes in the laundry and as a bleaching agent for cotton and linen in the textile industry. It is a strong oxidizing agent, hence used as an oxidizer in many industries. It is used as a disinfectant which is used for disinfecting water to make potable water. Sodium Hydroxide Sodium hydroxide is a whitish solid, available in flakes, pellets and granules. It is popularly known as caustic soda. It is soluble in a polar solvent such as water but insoluble in non-polar solvents such as ether.
Sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide crystal 3D ball structure
1. Preparation of Sodium Hydroxide Sodium hydroxide is synthesized through the chloralkali process. In this process, electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (commonly called brine), and the decomposition of brine takes place. Chlorine gas is deposited at the anode while hydrogen at the cathode. The final solution of sodium hydroxide is formed at the cathode. As NaOH (an alkali) and chlorine gas are present in the final product, this process is known as the chloralkali process.
2. Uses of Sodium Hydroxide It is used for the manufacturing of paper, soaps, and detergents. It is used for degreasing metals. It is used to remove sulphurous impurities from poor-quality crude oil by a process called caustic washing.
Baking Soda - Preparation, Properties And Uses
Sodium bicarbonate, also known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3 and the IUPAC designation sodium hydrogencarbonate. A sodium cation (Na+) and a bicarbonate anion (HCO3) combine to form this salt. Sodium bicarbonate is a white, crystalline substance that is commonly found as a fine powder. It tastes slightly salty and alkaline, like washing soda (sodium carbonate). Nahcolite is a type of natural mineral. It is found dissolved in many mineral springs and is a component of the mineral natron.
Baking soda is the common name of sodium bicarbonate. The chemical formula of baking soda is NaHCO3.
Baking Soda is also defined as Sodium Bicarbonate. The Medieval Egyptians first quarried Natron, a natural deposit which mainly consists of Na2CO3. They used it as soap. In the year 1971, NaHCO3 was first manufactured by a French chemist named Nicolas Leblanc. It was in the year 1846, John Dwight and Austin Church started a manufacturing unit to produce baking soda using sodium carbonate and carbon dioxide.
We can see various applications of chemistry that are being exhibited in every part of a household like in the bathroom, kitchen, etc. One such compound is Sodium bicarbonate, which is used mainly because of its versatility, usefulness and its cheap price.
Preparation of Baking Soda
Solvay process is used for the production of sodium bicarbonate and sodium carbonate industrially. In this process carbon dioxide, water, ammonia and brine solution in its concentrated form, are used as raw materials. This process is used mainly because it is inexpensive and less raw materials are used to produce necessary chemicals. The important chemical reaction that is used in the production of baking soda and sodium carbonate is:
CO2 + H2O + NH3 + NaCl → NaHCO3 + NH4Cl
2 NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
Carbon dioxide produced is recycled to produce NaHCO3
What is washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O)?
Washing soda is a chemical compound with the formula Na2CO3.10H2O. It is an inorganic hydrate of sodium carbonate. It was extracted from the ashes of plants growing in sodium-rich soils and hence the name soda ash. It is a white crystalline solid and a metal carbonate which is soluble in water.
Solvay Process- Preparation of Sodium Carbonate The steps involved in the manufacture of sodium carbonate are explained below:
Purification of Brine
Formation of sodium hydrogen carbonate
Formation of sodium carbonate
Recovery of ammonia
Step 1: Purification of Brine
A highly concentrated water solution of common salt is known as a brine solution. Concentrated brine is obtained by the process of evaporation and impurities like calcium, magnesium, etc are removed by the precipitation process. The concentrated brine solution undergoes filtration and is mixed with ammonia in the ammonia tower and the ammonia tower gets cooled.
Step 2: Formation of sodium hydrogen carbonate
In a carbonate tower, carbon dioxide is passed through an ammoniated brine solution.
NH3(aq) + CO2(g) + NaCl(aq) +H2O → NaHCO3(s) + NH4Cl(aq)
Step 3: Formation of sodium carbonate
Sodium Bicarbonate formed is heated to 300°C to get sodium carbonate.
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
Step 4: Recovery of ammonia
Ammonia can be recovered by treating the solution of NH4Cl with Ca (OH)2. This ammonia is again used in the Solvay process and CaCl2 is obtained as a by-product.
2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → 2NH3 + CaCl2 + H2O
Physical properties and chemical properties of sodium carbonate:
It is a crystalline solid which is white.
It exists as a monohydrated salt (Na2CO3.H2O), anhydrous salt (Na2CO3), heptahydrate salt (Na2CO3.7H2O) and decahydrate salt (Na2CO3.10H2O).
Sodium carbonate is basic in nature.
It has a melting point of 851°C.
In the presence of heat, it loses its water to form an anhydrous salt (soda ash).
Na2CO3.10H2O → Na2CO3.H2O → Na2CO3 (at 373 K)
Uses of Washing Soda: Used as a cleansing agent in industries and households.
It finds its application in paper, textile, soap, and detergent industries.
It is used in the process of softening water.
It is used in the manufacturing of glass.
It is one of the most important agents in laundries.
Get associated with the family of BYJU’S to understand the concepts in-depth with the help of an expert faculty.